RPMA, the full name of Random Phase MulTIple Access, the official Chinese translation for "random phase multiple access."
As the largest dark horse in the field of low-power WAN technology of the Internet of Things - RPMA technology has come to China!
As early as January of this year, John Horn, CEO of RPMA technology in the United States, personally visited Wuxi and planned to expand the Internet of Things infrastructure with RPMA as the core technology to the whole of China. At present, Ingenu has cooperated with Wuxi Military Intelligent Electric Co., Ltd. to establish Wuxi Jiuzhou Communication as the only authorized company of Ingenu to promote its RPMA technology and application in mainland China.
Introduction to RPMA technology
RPMA, the full name of Random Phase MulTIple Access, the official Chinese translation for "random phase multiple access", is a low-power wide area network (LPWA) technology in the Internet of Things.
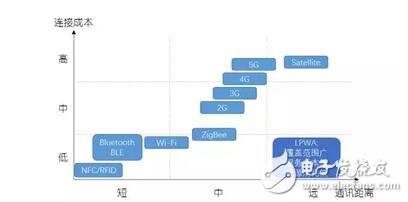
Figure 1: Coverage and connection costs of major communication technologies
What about LPWA?
LPWA, the full name of Low Power Wide Area, is a low-power wide-area network. The low-power wide-area network is a long-distance and low-power communication demand for the Internet of Things. In recent years, an Internet of Things wireless connection technology has a long transmission distance. The technical characteristics of low node power consumption, simple network structure, and low operation and maintenance cost. The emergence of low-power WAN technology has filled the gap in existing communication technologies and laid the foundation for the larger-scale development of the Internet of Things.
For consumer Internet of Things (IoT) applications, Wi-Fi, ZigBee, and Bluetooth are ideal near-range wireless networking technologies, but for the wider range of civil, industrial, and other IoT long-haul applications, cellular networks Or satellites can meet the requirements, but these technologies are not competitive in terms of cost, power consumption, and scalability. Therefore, in the context of the development of Internet of Things technology, low-power wide area network (LPWA) technology emerged.
Low-power wide area network (LPWA) technology is very versatile, and civil infrastructure such as parking lot resources, traffic flow control, utility monitoring, power distribution control, and environmental monitoring is just the beginning, such as crop growth monitoring and livestock migration. Agricultural applications also require wide area network coverage; asset monitoring and tracking, from taxis to frozen freight, requires regional, national, and even global coverage. Transportation infrastructure such as iron and highways also require wide-area surveillance; even consumer applications such as healthcare can benefit from WAN links that replace cellular phones.
LPWA has the characteristics of wide coverage, low service cost and low energy consumption. It can meet the connection requirements of low-speed data exchange frequency, low connection cost, convenient roaming network point switching and suitable complex environment in the IoT social environment. The ideal way of connecting things.
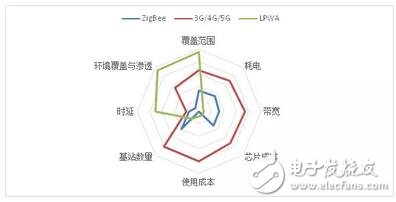
RPMA officially developed a low-power WAN access technology in the context of the development of Internet of Things technology. RPMA was developed by Ingenu, Inc., and Ingenu was established in 2008. The name of the company before September 2015 was ONRAMP. Ingenu provides developers with transceiver modules to connect to the RPMA network that the company and its partners have built around the world; these networks forward information from endpoints to the user's IT system. At the same time, RPMA is also suitable for customers who want to build a private network.
Under the joint operation of the RPMA terminal and the base station, the user can manage the capacity, data rate and range of their communication; the base station keeps synchronization with the terminal node that transmits the signal within the predefined time frame, and takes a random delay from the start of the time frame, the terminal node The spread spread factor is also selected based on the received signal strength.
The access point de-spreads, deinterleaves, and Viterbi decodes the received signal after receiving the data, and then performs a CRC check. As network usage increases, the access point can command the end node to reduce their transmitted signal strength to reduce the number of nodes it must process.
IngenuRPMA's security includes two-way authentication, 256-bit encryption and a 16-byte hash function, which effectively protects signal traffic; this solution allows the network to provide authorized software upgrades to endpoints and ensures information integrity and weight Send protection.
Incremental Encoder

Incremental Encoder,Linear Scale Encoder,Dual Concentric Rotary Encoder,Dc Servo Motor Encoder
Yuheng Optics Co., Ltd.(Changchun) , https://www.yhencoder.com