![]()
Test - lowercase jpg
![]()
Kaixin micro test
![]()
Test probe P100-M3
What are the experimental techniques for physical adsorption measurement?
Physical adsorption
Physical adsorption is a method used to study the interaction between a solid surface and gas molecules. The primary measurement involves determining the relationship between the amount of gas adsorbed by a sample and the pressure at a given temperature, known as the adsorption isotherm curve. This can be achieved through two main approaches: volumetric measurement (capacity method) and gravimetric analysis.
1) Gravimetric analysis involves using a sensitive microbalance combined with a pressure sensor to directly measure the mass change due to adsorption. However, it requires correction for buoyancy effects, which cannot be measured directly. This method is particularly useful when working within a limited temperature range around room temperature. Gravimetric vapor adsorption instruments can analyze water vapor, organic vapors, and various gases, including their adsorption and desorption rates. The vacuum gravimetric vapor adsorption instrument is a multi-station system that supports simultaneous analysis across 1–8 stations, making it ideal for research institutions and companies developing materials with specific adsorption properties. Due to its accuracy and reliability, gravimetric methods are widely adopted in high-end laboratories globally.
However, in gravimetric analysis, the adsorbate cannot be directly connected to a temperature control system, making it difficult to maintain accurate temperatures at low or high extremes. Therefore, measurements involving gases like nitrogen, argon, and helium at liquid nitrogen (77.35 K) or liquid argon (87.27 K) typically rely on volumetric methods instead.
2) The volumetric measurement method, also known as the vacuum volume method, uses calibrated volumes and pressure readings to calculate the amount of gas adsorbed. It relies on the principle of conservation of total gas volume, where the difference between the gas introduced into the sample tube and the free space is used to determine the adsorption amount. Both gravimetric and volumetric methods require the adsorption process to occur under static or quasi-equilibrium conditions. In quasi-equilibrium, gas is slowly introduced into the sample, and the desorption curve is obtained by gradually reducing the pressure. Achieving true equilibrium is one of the most challenging aspects of this process. To verify equilibrium, experiments are repeated at different gas flow rates; if consistent results are obtained, the data is considered reliable. This method provides highly accurate adsorption isotherms and is often preferred for detailed studies.
3) The continuous flow method is an alternative approach that differs from the quasi-static method. In this technique, a mixture of carrier gas (e.g., helium) and adsorbed gas (e.g., nitrogen) is continuously passed through a fluidized bed containing the sample. The adsorption of nitrogen causes changes in the gas composition, which are detected using a Thermal Conductivity Detector (TCD). This method is commonly used for fast analysis of single-site specific surface areas.
Bethes Instrument Technology (Beijing) Co., Ltd. is a leading manufacturer of physical adsorption analysis instruments. As a national high-tech enterprise, it integrates R&D, production, sales, technical support, and after-sales services. With over 5,000 square meters of factory space and a registered capital of 5 million yuan, the company has established itself as a leader in China's market.
The 3H-2000 series of physical adsorption instruments developed by Bethes Instruments is a well-known domestic brand, originally launched in 2000. After years of innovation and development, these instruments have reached top-tier performance levels both domestically and internationally. Many models even surpass imported alternatives, making them a benchmark in high-precision physical adsorption analysis.
Bethes Instruments has a dedicated technical team and holds 30 technical patents. It was recognized as a Beijing high-tech enterprise in 2009 and received ISO9001 quality system certification in 2011. The company has also benefited from government innovation funds, further strengthening its position in the industry.
With offices in Shanghai, Guangzhou, and Wuhan, the company provides on-site testing and technical support. Each office is equipped with prototype instruments and has 2–3 technicians and engineers to ensure timely assistance for customers.
In 2015, the company expanded to a new modern factory, offering advanced equipment, better production conditions, and improved testing environments. The facility includes specialized labs such as high-pressure adsorption, steam adsorption, laser welding chambers, and helium leak detection rooms, ensuring top-quality instruments and long-term growth.
For after-sales service, Bethes has a dedicated team of 10 full-time engineers who provide installation, training, and maintenance. Over 90% of users can receive support within 24 hours. The company also offers free software upgrades, regular follow-ups, and warranty services to ensure customer satisfaction.
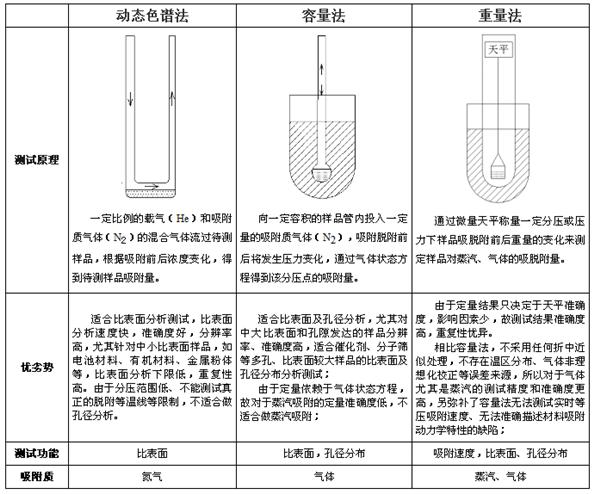
Reference comparison of three test methods
Durable Full-Range Speakers,Performance Full Range Speaker,Steel Concert Speaker,Flexible Speaker Horn
