How to use the technology of dimming LED light source? How do we master it? To answer the above questions, we must first understand the volt-ampere characteristics of LED.
Volt-ampere characteristics of LED
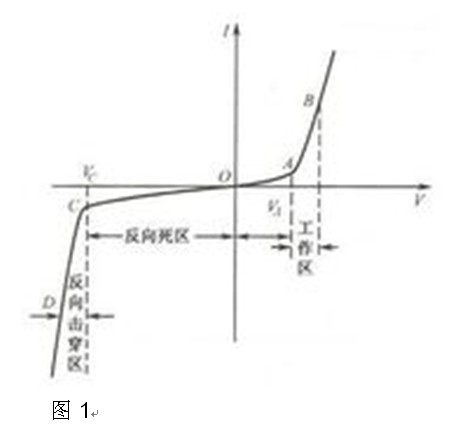
The so-called volt-ampere characteristic of the LED, that is, the current flowing through the LED PN junction (refer to the LED revolution, revolution), the current varies with voltage, which can be visually displayed on the oscilloscope (Figure 1), one The complete volt-ampere curve includes forward and reverse characteristics. In general, the reverse characteristic curve changes steeply. When the voltage exceeds a certain threshold, the current rises exponentially, which breaks down the LED PN junction. The forward voltage of the LED is also determined by its forward current. From the volt-ampere characteristics of the LED (Figure 1), the change in forward current causes a corresponding change in the forward voltage. Specifically, the decrease in the forward current also causes a decrease in the forward voltage. Therefore, when the current is turned down, the voltage of the LED is also reduced, which changes the relationship between the power supply voltage and the load voltage.
Therefore, from the volt-ampere characteristics of the LED, we can know that the dimming of the LED light source can not be achieved simply by reducing the input voltage or input current of the LED. In addition, the waveform of the sine wave of the LED is different from the waveform of the incandescent lamp, so it cannot Simply by changing its conduction angle, the purpose of changing its effective value (effective dimming) is achieved.
To make it easier for everyone to understand the above points, examples are as follows:
For example, in an LED lamp with an input of 24V, eight 1W high-power LEDs are connected in series. When the forward current is 350mA, the forward voltage of each LED is 3.3V, then 8 series is 26.4V, so the load voltage is higher than the input voltage, so a constant current source of >24V should be used. However, in order to dim, the current is reduced to 100mA. At this time, the forward voltage is only 2.8V, and the 8 series is 22.4V. The load voltage becomes lower than the input voltage, so the constant current source of >24V cannot be used at all. Work, and finally the LED will flash.
At this time, you may use a step-down (wide voltage) constant current source, such as a 10V-30V constant current source for dimming, but this step-down (wide voltage) constant current source is adjusted to a low level. The forward voltage and the load current of the LED also become very low, so the step-down ratio is very large, which exceeds the normal working range of the buck-proof (wide voltage) constant current source, and also makes it inoperable and flickers. . In addition, the step-down (wide voltage) constant current source can work for a long time at low brightness, which can reduce its efficiency and increase the temperature rise, because the efficiency of the step-down (wide voltage) constant current source is low. The pressure ratio is related, the larger the step-down ratio is, the lower the efficiency is, and the greater the power consumption of the loss on the chip, which may damage the life of the constant current source and the LED light source. Many people do not understand the problems, but also always go to the dimming circuit to find the problem, it is useless.
LED thyristor dimming
Conventional incandescent and halogen lamps are typically dimmed with a thyristor. Because incandescent and halogen lamps are purely resistive devices, it does not require that the input voltage be a sine wave, because its current waveform is always the same as the voltage waveform, so regardless of how the voltage waveform deviates from the sine wave, just change the effective value of the input voltage. You can dim.
However, the adjustment of the thyristor dimming to the LED light source has the unexpected problem that the LC filter at the input causes the thyristor to oscillate. This oscillation does not matter for the incandescent lamp because the thermal inertia of the incandescent lamp makes The human eye does not see this oscillation at all, but it produces audible noise and flicker for the LED's drive power. In addition, thyristor dimming destroys the sine wave waveform, which reduces its power factor value (usually below 0.5), so thyristor dimming greatly reduces the system efficiency of the LED. Moreover, the waveform of the thyristor dimming increases the harmonic coefficient, and the non-sinusoidal waveform will cause serious interference signals (EMI) on the line to pollute the power grid, which will seriously smash the power grid.
Read here, you may ask: "Reducing voltage or current and thyristor dimming is not suitable for LED light source dimming, so what is the most appropriate?".
Is it analog (1-10V) dimming? No. Analog dimming faces a serious challenge, which is the accuracy of the output current. Almost every LED driver uses a series resistor to identify the current, while tolerances, offsets, and delays in analog (1-10V) dimming drivers result in a relatively fixed error, which in turn reduces The accuracy of the output current, the final output current cannot be specified, controlled or guaranteed. Therefore, the dimming effect of the LED light source is ensured, and an important point is to reduce the output current error and improve the current accuracy in a closed loop system.
The PWM (Pulse Width Modulation) dimming method can solve the above problem well, because the LED is a diode, which can realize fast switching. It can allow switching speeds of up to microseconds, which is unmatched by any illuminating device. Therefore, as long as the power supply is changed to a pulse constant current source, the brightness can be changed by changing the pulse width. This method is called pulse width modulation (PWM) dimming. This dimming method is like a sluice with a switch of up to microseconds. Because the sluice switch frequency is very fast, we can't identify the state of its switch with the naked eye. As a result, we can only pass the amount of downstream water. Identify the speed of its switching frequency. In addition, since the sluice changes the duty ratio of the output water flow (the effective flow rate of the water flow), and does not change the instantaneous water pressure and the instantaneous flow rate of the water flow, the switching operation of the sluice up to microseconds does not affect the work of the hydroelectric power generation, because the moment The water pressure and instantaneous flow rate are unchanged, and the amount of water flowing down and the total amount of power generation are changed. Therefore, the PWM (Pulse Width Modulation) dimming method does not change the instantaneous voltage and instantaneous current of the input LED PN junction, and changes the duty ratio of the output current, thereby changing its brightness.
Therefore, the LED PWM (Pulse Width Modulation) dimming method has the following advantages:
1. No LED chromatogram offset will occur because the LED is always operating between full-scale current and zero.
2, has a very high dimming accuracy, because the pulse waveform can be controlled to a very high precision, so it is easy to achieve one-tenth of the accuracy.
3. Even if the light is dimmed in a wide range, no flicker will occur. Since the operating conditions of the constant current source (boost ratio or step-down ratio) are not changed, it is less likely that overheating and the like occur.
4. It can be combined with digital (DALI/DSI/DMX 512) control technology for control, because the digital control signal can be easily converted into a PWM signal.
Although LED PWM (Pulse Width Modulation) dimming has many advantages, there are two issues to be aware of:
1, the choice of pulse frequency, because the LED is in a fast switching state, if the operating frequency is very low, the human eye will feel flicker. In order to make full use of the visual residual phenomenon of the human eye, its operating frequency should be higher than 100 Hz, preferably 200 Hz.
2, eliminate the whistling caused by dimming, although the eyes above 200Hz can not be detected, but up to 20kHz is the range of human hearing. At this time, it is possible to hear the sound of the silk. There are two ways to solve this problem. One is to increase the switching frequency to above 20 kHz and jump out of the human ear. Another method is to find out the sounding device and process it.
At present, some manufacturers of LED dimmable power supplies, drivers and digital control systems have solved the above problems well. For example, Tridonic's LED dimmable power supply and driver adopt PWM (Pulse Width Modulation) modulation. Optical technology (Figure 2), its control signals are all using DALI (Digital Addressable Lighting Interface) technology, combined with digital lighting control system, to achieve a fully digital LED control product line. In addition, TRIDONIC's latest LED light engine products based on PL-LED technology (Figure 3). PL-LED refers to TRIDONIC's LED phosphor innovation technology, which can change the color and color temperature in the same LED light source. At the same time, the fixed color temperature (for example: 2700K-6200K) or color can be selected by software (for example: RGB). And carry out dimming control, currently the highest level of digital dimming technology for LED applications.

figure 2

image 3
LED digital (DALI) dimming interface
Good LED light source dimming technology needs good LED control signal technology to match and cooperate, in order to become an effective, stable and reliable system. As mentioned earlier, the LED PWM (Pulse Width Modulation) dimming method has an outstanding advantage, and the digital control signal can be easily converted into a PWM signal. Among the digital control signals for illumination, DALI (Digital Addressable Lighting Interface) has unparalleled superiority in other lighting digital control signals, and is also the mainstream and open international standard for digital control signal applications in the lighting industry. Therefore, the matching of PWM (Pulse Width Modulation) dimming mode and DALI (Digital Addressable Lighting Interface) can be described as “good horse with good saddleâ€, each playing its own advantages, PWM (pulse width modulation) dimming technology to solve The final dimming problem of LED light sources, DALI (Digital Addressable Lighting Interface) technology solves the control, feedback and networking of each LED luminaire.
The biggest feature of DALI (Digital Addressable Lighting Interface) technology is that individual luminaires have independent addresses. DALI system software can be used for precise dimming and switching control of single lamps or any group of lamps, regardless of whether they are on strong power. Is the same loop or a different loop. That is, the lighting control is independent of the high-power circuit. The DALI system software can independently address single or multiple lamps on the same high-voltage circuit or different circuits, thereby achieving separate control and arbitrary grouping. This concept brings great flexibility to the lighting control, users can design the lighting solution to meet their needs as needed, and even modify the control requirements during the operation after the installation, without having to do any work on the line. change.

Figure 4