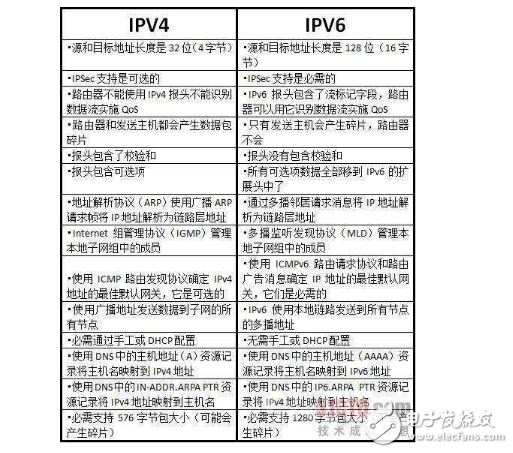
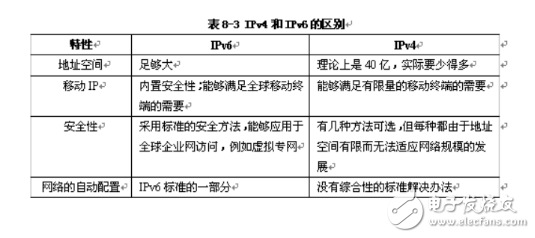
Just like humans communicate, computers also need to follow specific rules to exchange information. These rules are known as network protocols. The protocol suite used by the global Internet today is the TCP/IP protocol family. IP, or Internet Protocol, is a key protocol at the network layer of this suite and serves as the core of the entire TCP/IP system. In Windows 7 and later versions, when configuring an IP address, users often see both IPv4 and IPv6 options. This is different from earlier systems like Windows XP, which only displayed the TCP/IP protocol. Many people find this confusing and wonder about the differences between IPv4 and IPv6. In this article, we'll explain the main distinctions between these two protocols. The current global Internet relies on the TCP/IP protocol suite. IP is the primary protocol at the network layer and has been in use for over 30 years. The current version of the IP protocol is IPv4, which uses 32-bit addresses. This allows for approximately 4.3 billion unique IP addresses. However, with the rapid growth of the Internet, the demand for IP addresses has increased significantly, leading to a shortage of available IPv4 addresses. By 2005–2008, it was predicted that all IPv4 addresses would be exhausted. IPv4 is the fourth version of the Internet Protocol and has been the foundation of the modern Internet for decades. It uses 32-bit addresses, meaning there are about 4.3 billion possible unique IP addresses. However, due to the fast expansion of the Internet, the number of available IPv4 addresses has become limited, causing concerns about future scalability. IPv6 is the next generation of the Internet Protocol, designed to replace IPv4. It was developed because IPv4’s address space was too small to support the growing number of devices connecting to the Internet. IPv6 uses 128-bit addresses, providing an almost unlimited number of IP addresses—so many that even if every square meter of Earth had thousands of addresses, there would still be plenty left. Beyond just expanding the address space, IPv6 also improves security, supports better quality of service (QoS), enhances mobility, and simplifies network configuration. IPv4 is the original Internet Protocol that formed the basis of the Internet we know today. Its successor, IPv6, was created to solve the limitations of IPv4, especially the exhaustion of IP addresses. While IPv4 uses 32-bit addresses, IPv6 uses 128-bit addresses, making it much more scalable. IPv6 also brings improvements in security, performance, and ease of management. One of the biggest advantages of IPv6 is its massive address space. With 128 bits, IPv6 can provide more than 3.4 x 10^38 unique addresses—enough to assign an IP address to every grain of sand on Earth and then some. In addition to this, IPv6 includes features like built-in support for multicast, improved security through IPsec, and auto-configuration, which makes network setup easier and more efficient. IPv6 offers several significant improvements over IPv4. First, it provides a vastly larger address space, which ensures that we won’t run out of IP addresses anytime soon. Second, IPv6 simplifies routing by using a more efficient structure, which helps reduce the size of routing tables and improves performance. Third, it includes enhanced security features, such as mandatory encryption and authentication through IPsec. Additionally, IPv6 supports better quality of service (QoS), making it ideal for real-time applications like video streaming and online gaming. Another major advantage is auto-configuration, which allows devices to automatically obtain an IP address without needing a DHCP server. This makes network management much easier, especially in large-scale environments. Finally, IPv6 is designed to be more secure and efficient, making it the preferred choice for future networks. Although IPv6 is not backward compatible with IPv4, most modern systems support both protocols simultaneously. This dual-stack approach allows for a smooth transition from IPv4 to IPv6. As more services and devices adopt IPv6, it will eventually become the standard, offering better performance, security, and scalability for the Internet of tomorrow. For both home and business users, it's essential to ensure that new network devices support IPv6. While IPv4 addresses are still available, their scarcity is increasing, and reliance on them may lead to higher costs and technical challenges in the future. Therefore, it's wise to plan for IPv6 now and gradually migrate to it. In conclusion, while IPv4 has served us well for many years, it is no longer sufficient to meet the demands of today’s growing Internet. IPv6 represents a major advancement in network technology, and its adoption is inevitable. By understanding the differences between IPv4 and IPv6, you can make informed decisions about your network infrastructure and prepare for the future of the Internet.
Yuhai company develop and produce of
various rings sizes, bearing variety of electrode and metallisation
configurations. This variety of Rings is fabricated from various material
formulations for applications such as high power, sensitivity, stability.
Features
·
• electrode type on request
·
• Surface roughness on request, for specific demanding application
·
• Thickness/Radial frequency tuning
available on request
Applications include
• Sensors
• Welding
•
Ultrasonic
cleaning
• Precise Measurement
• Ultrasonic scalpel
• Cauterisation
• Phacoemulsification
•
Therapeutic
ultrasound
• Accelerometers
Dimension range
Outer diameter
3-180mm
Inner diameter
1-150mm
Thickness
0.2-25mm
Piezo Ring,Pzt Ring,Piezoelectric Ceramic Ring,Piezo Ceramic Ring Zibo Yuhai Electronic Ceramic Co., Ltd. , https://www.yhpiezo.com