BigDog robot sensor is powerful
Boston Dynamics is a remarkable company that originated from the Massachusetts Institute of Technology. It has developed a wide range of advanced robots, including those that mimic the movement and agility of animals, as well as others capable of climbing vertical surfaces and navigating tight spaces. These robots are designed to enhance and extend the capabilities of both humans and animals, much like a superhuman.
This article highlights one of Boston Dynamics' most famous creations: BigDog, a four-legged robot that stands about three feet tall and three feet long, weighing 240 pounds. It is capable of traversing muddy slopes while carrying a load of 340 pounds.

BigDog is a quadrupedal robot with a dog-like appearance, standing at three feet high and three feet long, and weighing 240 pounds.
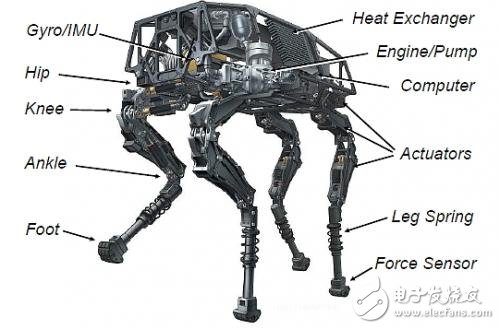
The robot is equipped with 50 sensors that provide real-time data to the onboard computer, helping it maintain balance and direction. These sensors also allow the robot to recover if it falls or gets off course.
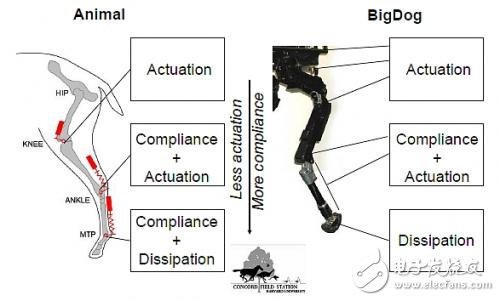
BigDog uses a 15-horsepower micro-racing engine. This two-stroke, single-cylinder engine operates in a water-cooled manner and powers a hydraulic system that controls the movement of its four legs. The legs are designed to replicate the natural motion of large mammals, giving the robot a lifelike gait.
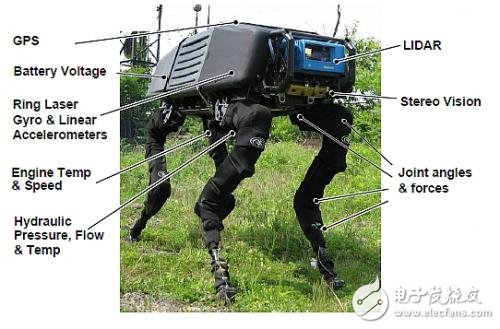
Important external features play a key role in BigDog's performance. Among these are inertial sensors, which measure posture and acceleration, and joint sensors that monitor the force and movement at each joint. The onboard computer processes this data to estimate how the robot moves through space.
Other sensors track the robot’s dynamic balance, including hydraulic pressure, flow, temperature, engine speed, and temperature. These systems work together to ensure stability and efficiency during operation.
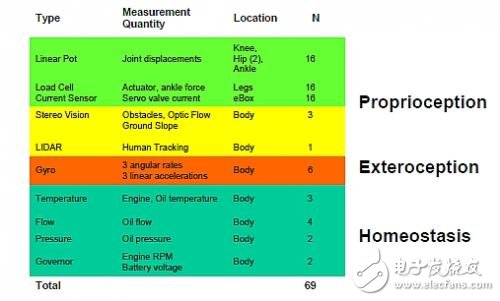
Robots like BigDog rely on an array of sensors to perceive their environment and interact with it effectively.
In the paper "The Body and the Senses: The Perception of Space" by Brian Massumi, he discusses three levels of bodily perception: external sensations, proprioception, and inner feelings. External sensations include sight, hearing, touch, taste, and smell. Proprioception involves the body's ability to sense its position and movement in space, converting action and relaxation into muscle memory. Inner feelings refer to the immediate recording of sensory stimuli before they are fully processed by the brain. These layers correspond to different ways the body interacts with the world, offering a deeper understanding of how we experience our surroundings.
Oem Scan Module,Oem Barcode Scanner Module,Barcode Oem Module,Scanner Module
Guangzhou Winson Information Technology Co., Ltd. , https://www.barcodescanner-2d.com